Metal corrosion by seawater is a serious problem, and countermeasures have
been sought by related industries for years.
To solve this problem, YOKOTA has developed the material YST130N based
on our many achievements and experience in this area. YST130N has excellent
seawater resistance, and also excellent corrosion resistance to a wide
range of corrosive liquids including corrosive hot water at geothermal
generation plants and hot springs among others.
|
Features
|
|
|
Excellent crevice corrosion resistance and pitting corrosion resistance
in seawater environments.
|
|

|
Excellent corrosion resistance to general chemical liquids.
|
|

|
Highly suitable for seawater containing sand and slurry due to its excellent
wear resistance.
|
|

|
Heat and high temperature resistance.
|
|

|
Can be formed into any shape because it is made of casting.
|
|

|
Easily welded by covered arc or TIG welding without preheating or residual
heating.
|
|

|
Being attracted to a magnet, it can be easily located or sorted using the
magnet.
|
|

|
Due to the above, drastic reduction in equipment and maintenance costs
is possible.
|
|
Note 1:
Most of the seawater pump parts are made of stainless steel casting and
gray cast iron. As gray cast iron pumps require a lot of maintenance, the
share of stainless steel pumps has been increasing. However, a lot of local
corrosion in the form of crevice corrosion and pitting corrosion occurs
in conventional stainless steel. Though crevice corrosion is similar to
pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion occurs more often than pitting corrosion
in systems with crevices.
|
|
Pitting corrosion resistance
|
| 5% ferric chloride 40 deg C, 50 hours |
|
|
|
Crevice corrosion resistance
|
|
|
|
|
Corrosion resistance to liquids other than seawater
In addition to seawater, YST130N has excellent corrosion resistance to
a wide range of corrosive liquids including hot springs water, corrosive
hydrothermal liquids, chemicals and others.
The high corrosion resistance of YST130N has been proven consistently in
a number of comparative corrosion resistance tests, detailed below, carried
out throughout Japan.
Even when compared with materials such as Hastelloy C equivalents, currently
the most corrosive resistant material known, YST130N proves to be equally
efficient. Moreover, because it is comparatively more economic, YST130N
has gained a widespread reputation for excellent cost performance.
|

|
Field test with actual liquids: Kusastsu Hot Springs
|
At the Kusastsu Hot Springs in Gunma Prefecture, well known for its acidic
hot springs that contain hydrogen sulfide, pumps made of normal materials
quickly become corroded.
Under these conditions, a comparative corrosion resistance test using various
materials and a operational test of a pump made from YST130N were performed.
|
Kusatsu Hot Springs - Spring water composition |
|
|
Water temp.
|
94.2 deg C
|
|
PH
|
l.7
|
|
Spring water composition
|
Acid chlorides, sulfates
|
|
Main elements
(mg/kg)
|
Positive ions
|
Sodium ions
|
149
|
|
Magnesium ions
|
57.9
|
|
Calcium ions
|
93.2
|
|
Negative ions
|
Chloride ions
|
901
|
|
Sulfate ions
|
826
|
|
Dissolved gas
|
Free hydrogen sulfide
|
0.3
|
|
| (1) Test pieces immersed in hot springs reservoir (Test period: May 26
to Dec. 2, 1999) |
|
Test conditions
|
Test results: Amount of damage due to corrosion
|
|
|
|
By comparing the corrosion rates of the different materials, it is clear
that YST130N proves to have the highest level of corrosion resistance.
| (2) Pump operation test: Hot springs pump room (Operating period: Mar.
6 to Sept. 6, 2000) |
|
Test pump
|
Test pump external view
|
|
|
Type
|
YOKOTA Centrifugal Pump UEN-0420
|
|
Specs.
|
6m3/h x 55m x 3000min-1 x 5.5kW
|
|
Material
|
YST130N
|
|
Shaft seal
|
Gland packing
|
|
Operation time
|
4,416 hours (Mar. 6 to Sept. 6, 2000)
|
|
|
|
|
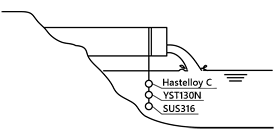
Open inspection photo after a period of time |
|
|
|
|
|
Casing
|
|
Suction cover
|
|
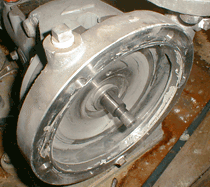
Impeller front view |
|
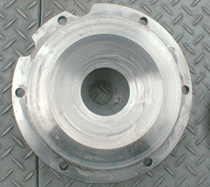
Impeller rear view |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As seen in the photos, the pump constructed using YST130N exhibits no signs
of corrosion, clearly demonstrating its perfect suitability for hot springs
use.
|

|
Pump operation test: Kaike Hot Springs
|
At the Kaike Hot Springs in Tottori Prefecture, well known for its salt
springs, pumps made of normal materials will quickly become corroded.
Under these conditions, a pump constructed using YST130N has been operating
normally for a period of over ten years without signs of corrosion, proving
once again, the perfect suitability of this material for use at these hot
springs also.
|
Kaike Hot Springs - Spring water composition
|
Pump operation results
|
|
|
Water temp.
|
79.8 deg C
|
|
Spring water
composition
|
Sodium and calcium chlorides
|
|
Main elements
(mg/kg)
|
Positive
ions
|
Sodium ions
|
2156
|
|
Magnesium ions
|
40
|
|
Calcium ions
|
1658
|
|
Negative
ions
|
Chloride ions
|
5846
|
|
Sulfate ions
|
669.8
|
|
|
Pump type
|
YOKOTA Self-Priming Centrifugal
Pump UHN
|
|
Bore
|
40-100mm
|
|
Material
|
YST130N
|
|
Shaft seal
|
Gland packing
|
|
Pumps in
operation
|
34 pumps (First put into operation in 1980)
|
|
Operation results
|
Over 10 years of operation with no corrosion
|
|
|

|
Field test with actual liquids: Waste incineration plant toxic gas removal
unit
|
A "toxic gas removal unit" that sprays caustic soda (NaOH) on
toxic gases to collect the toxic components is one example of devices used
to remove toxic gases (such as hydrogen chloride, sulfur oxide, and nitrogen
oxide) generated during waste incineration. The interior of this type of
unit presents an especially harsh environment where corrosion easily occurs.
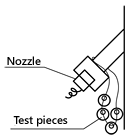
In order to compare their relative corrosion resistance, test pieces of
various materials were suspended inside this type of unit and positioned
so that they would be exposed to both the caustic soda sprayed from the
nozzle and the gases that pass through the unit.
|
Test specs.
|
|
|
|
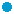
Test location
|
H City Environmental Affairs Bureau A Plant
|
|
Test equipment
|
Waste incineration toxic gas removal unit No. 2
|
|
Test conditions
|
Exhaust gas: 260 deg C, HCl, SO3
Liquid: 70 deg C, NaOH 8%, PH 7-8
|
|
Exposure time
|
9,288 hours (387 days)
|
|
|
Hanging test pieces
|
Test results: Amount of damage due to corrosion and wear
|
|
|
|
The metallic surfaces of SCS10 and SUS316 are clouded due to corrosion.
However, the metallic sheen remains on YST130N and Hastelloy C equivalent
material, proving their suitability for this type of equipment.
The performance of YST130N is especially outstanding.
The fact that the amount of wear includes that from the test pieces rubbing
against each other gives further proof of YST130N's extremely strong durability.
|

|
Field test with actual liquids: Human-waste treatment plant deodorization
unit
(alkali cleaning tower)
|
One example of a deodorization system to remove the noxious fumes created
when treating human waste consists of gas being passed through an acid-cleaning
tower, an alkali-cleaning tower, and then an active carbon-absorption process
tower. Within this system, the interior of the alkali-cleaning tower, which
utilizes sodium hypochlorite (NaClO), presents an especially harsh environment
where corrosion easily occurs.
Test pieces of various materials were placed inside of an alkali-cleaning
tower to compare their relative corrosion resistance.
|
Test specs.
|
Test results: Amount of damage due to corrosion
|
|
|
Test location
|
H City Environmental Affairs Bureau D
Treatment Plant
|
|
Test equipment
|
Human-waste treatment plant deodorization unit - Alkali cleaning tower
|
|
Test conditions
|
Liquid: 20 deg C, NaClO 12% + NaOH 25%, PH 8-9
|
|
Exposure time
|
6,660 hours (278 days)
|
|
|
The metallic surfaces of SUS316 are clouded and streaks of pitting have
developed due to corrosion.
However, the metallic sheen remains on YST130N and Hastelloy C equivalent
material, proving their suitability for this type of equipment.
The performance of YST130N is especially outstanding.
The above tests prove conclusively that YOKOTA's duplex stainless steel
material, YST130N, has excellent corrosion resistance to, of course, seawater,
but also hot springs water, corrosive hydrothermal liquids, chemical liquids,
and corrosive gases.
|
Note 2:
Metallographic structure
Duplex stainless steel is a stainless steel that is composed of two types
of compounds, austenite (white part) and ferrite (gray part).
|
 |
For details on items such as corrosion and wear resistance data, please
refer to this page.
Supply record
|
|
|
|
Central Fisheries Research Center (Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and
Fisheries of Japan),
Fisheries research institutes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Food processing plants, Salt manufacturing plants
|
|
|
|
|
Seawater desalination plants
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|